A certain therapist with 50 years of experience once remarked: "When I started working, there was not a single young patient with osteochondrosis at the site. And today, almost every second of 30-year-olds has this problem. "
Osteochondrosis - a disease caused by the deposition of salts in the spine
Wrong. The intervertebral disc consists of the nucleus pulposus, the annulus fibrosus and the hyaline cartilage covering it from above and below.
With the destruction of these elements, the balance between the load on the spinal column and the ability to carry it is disturbed. As a result, the vertebrae begin to compress the adjacent nerve and muscle tissues, grow along the edges, forming the so-called. osteophytes, which emit a characteristic crunch when moving (patients mistakenly explain it as "salt deposition").
If the back and neck hurt, then this is exclusively osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is not the only cause of back pain. This diagnosis is often made by patients themselves. However, in addition to this pathology, which is part of the group of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine, there is also osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and it is possible to differentiate only after a comprehensive examination.
- Degenerative-dystrophic changes occur in 30-50% of cases in 30-40-year-olds, in 75-100% of people over 40 years old.
- These pathological processes account for 20. 4% of the total disability from diseases of the osteoarticular system.
- Long walk is bad for the spine
Vice versa. Motor activity has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the spinal column: it maintains muscle tone, preserves intervertebral mobility, stimulates blood circulation and metabolism. In the progression of the disease, hypodynamia and a long stay in one, especially uncomfortable position are "guilty".
Another thing is if an overweight person walks a lot, wears heavy things, then the spine experiences an increased load.
Flat feet contribute to the development of osteochondrosis
Right. The arches of the foot, as well as the physiological curves of the spine, are designed to absorb shock loads when walking, running, jumping. If the foot does not provide adequate protection when interacting with the support, then the spinal column receives an additional load, which significantly impairs the nutrition and functioning of its structures, and accelerates the development of the disease.
Back pain is the only symptom of the disease.
Not certainly in that way. As a rule, patients complain of constant aching pain in the back, often accompanied by numbness and aches in the limbs. Over time, if left untreated, the muscles of the limbs atrophy, the joints of the spine become less mobile, muscle spasms appear.
Such an acute condition occurs due to arterial spasm as a response to the effects of bone growths, as well as due to disc herniation, arthrosis of the intervertebral joint, as a reflex reaction to irritation of the spinal receptors.
- If a person suffers from coronary or cardiovascular pathology, then vertebral artery syndrome will aggravate the course.
- With osteochondrosis of the thoracic region, pain in the chest is disturbing (feeling as if a stake was stuck there) - in the area of \u200b\u200bthe heart and other internal organs; with lumbosacral lesions - in the lower back (irradiation to the sacrum, lower limbs, sometimes to the pelvic organs).
- If complications of osteochondrosis develop (herniated intervertebral discs, bone growths, spondylolisthesis, spondylarthrosis), then nerve root damage is noted - the pain becomes shooting, sensitivity worsens, weakness appears in the innervated muscles, and the severity of reflexes decreases.
- Osteochondrosis can cause dysfunction of various organs and tissues.
With osteochondrosis, the risk of circulatory disorders in the cerebellar, stem and occipital regions of the brain is increased.
A constant headache appears - first in the back of the head, then spreads to the region of the crown and temples, aggravated by neck movements (more often in the morning).
Elderly people with a sharp turn of the head may lose consciousness. This is preceded by dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision and hearing, nausea, vomiting.
Sometimes there is pain in the region of the heart - long, pressing, boring. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, especially in the elderly and senile age, soft tissues often change - they become more dense.
Degenerative processes in the spinal column can cause congestion in the gastrointestinal tract, disruption of the bronchopulmonary system, which is fraught with inflammatory and other ailments.
Vegetovascular dystonia, intercostal neuralgia - consequences of osteochondrosis
Not certainly in that way. Osteochondrosis can be one of the reasons (by far not the only one) for the development of these diseases.
When the intervertebral discs are "erased" and osteophytes grow, the intervertebral foramina, the canal of the vertebral artery narrow and deform, and this leads to the infringement of various structures.
In particular, when the nerve roots are compressed, signs of intercostal neuralgia appear, and when the vertebral artery is compressed, the same symptoms appear as with vegetative-vascular dystonia.
It is impossible to cure osteochondrosis
Indeed, the structures of the spinal column that have undergone degenerative changes cannot be fully restored. Nevertheless, adequate complex treatment can eliminate the symptoms of the disease, stop the development of pathology and avoid complications.
In case of problems with intervertebral discs, it is useful to warm up sore spots
Wrong. Temperature fluctuations, especially extreme ones (for example, a beginner's trip to the bath), can cause a serious exacerbation. Moderate thermal procedures are used in complex treatment, but they must be prescribed by a doctor.
If, with osteochondrosis of the cervical region, circular movements of the head are performed, the state of health will worsen
Right. These exercises are best done for prevention - they help maintain the range of motion in the intervertebral joints. With severe osteochondrosis, careless circular movements can aggravate vertebral artery syndrome, radiculopathy, etc.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are essential for treatment
Not really. During the period of remission or when the pain is not strong, conservative therapy is carried out (physio-, reflex- and manual); physical therapy, traction techniques are used. Drug treatment is indicated during an exacerbation and is aimed at relieving pain, relieving the inflammatory process and accelerating metabolic processes (intramuscular or intravenous injections).
Among the most effective agents are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which are prescribed to relieve inflammation and pain; with severe pain, novocaine blockades are used; steroid drugs (epidural, intramuscular injections); NSAIDs in the form of ointments, gels and creams with analgesic and irritating effects; muscle relaxants - to relieve muscle spasms; B vitamins - to improve metabolic processes in the spine (B1, B6, B12).
Osteochondrosis can lead to serious consequences
Yes. Due to compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots, osteochondrosis can cause paralysis, and if the vertebral artery is infringed, it can cause loss of consciousness.
Exercises to "stretch" the spine help to improve the condition
Traction, or traction, allows you to increase the intervertebral space, relieve pain and restore the anatomically correct shape of the spine. However, the individual load must be correctly calculated. "Busting" can lead to a reflex contraction of the paravertebral muscles and worsen the condition.
Only a traumatologist-orthopedist has the right to treat osteochondrosis
Wrong. Most patients are seen by a neurologist, with a significant severity of the pathology - by a neurosurgeon or an orthopedic vertebrologist.
A local therapist can also prescribe drug therapy to stop an exacerbation.
Spinal osteochondrosis: causes and treatment
Up to 76% of people experience back pain every year. This statistic affects people of all ages and professions. The causes of pain can be different, one of them is osteochondrosis of the spine.
Due to a sedentary lifestyle, osteochondrosis of the spine is becoming more common, and it is not always possible to defeat it on your own. Let's talk about why it occurs and how to deal with it.
What is spinal osteochondrosis
There are several different views on the definition. Some experts believe that it is more correct to use the general name - dorsalgia, or non-specific back pain.
Difficulties in definition are also associated with the fact that a variety of specialists work with this disease - neurologists, orthopedists, neurosurgeons and general practitioners.
Sometimes a person diagnosed with osteochondrosis of the spine turns to a cardiologist, since the manifestations of the disease are very similar to pain in the heart.
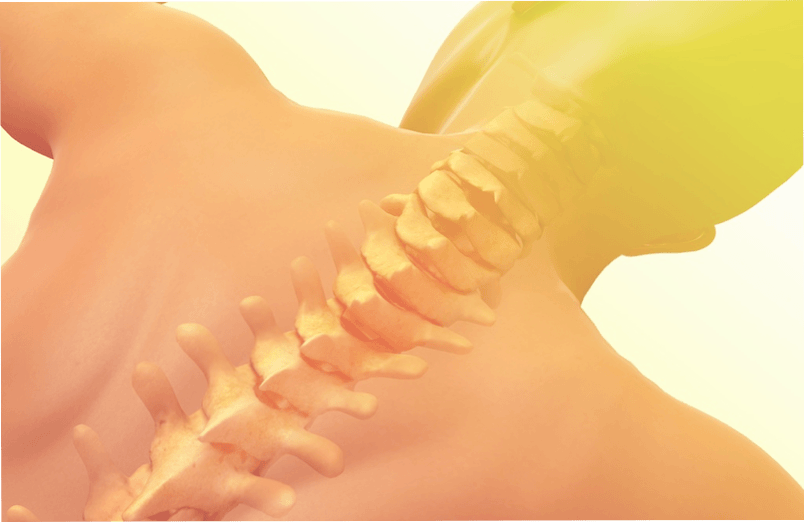
The term "osteochondrosis of the spine" was proposed by Hildebrandt in 1933 as a multifactorial degenerative disease of the spinal motion segment (as defined by Popelyansky). What is the spinal motion segment? These are two vertebrae located one above the other, and between them is an intervertebral disc.
Thanks to this articulation, the human spine can bend and unbend, bend and twist. But as a result of various reasons, the intervertebral discs lose their properties, undergo degeneration, and then gradually changes affect the vertebrae themselves.
That is, the essence of osteochondrosis of the spine is the gradual destruction of the intervertebral discs.
Osteochondrosis can develop in any part of the spine.
Due to the heavy load, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is most common. The symptoms are:
- lower back pain, which may be sharp or dull, constant, may increase with movement;
- pain can be given to the legs, pelvic organs, to the sacrum;
- in severe cases, there may be a violation of sensitivity or mobility, atrophy of the muscles of the lower extremities.
The second most common is cervical osteochondrosis, which is more often associated with prolonged uncomfortable head position, for example, when working at a computer or with documents. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is manifested by the following symptoms:
- headaches and dizziness, migraines;
- visual or hearing disorders, flashing "flies" before the eyes;
- pain can radiate to the back of the head, shoulders, collarbones;
- possible violation of sensitivity in the hands.
Less often, osteochondrosis affects the thoracic spine, since the vertebrae are inactively connected to each other. A lesion in this area can masquerade as heart or lung disease. Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis of the spine:
- pain in the back at the level of the shoulder blades, in the chest, which can increase with bending, turning, during inhalation or exhalation;
- skin sensitivity disorders.
Regardless of the level of damage, pain in osteochondrosis of the spine can increase with pressure on those vertebrae that are involved in the process.
With the defeat of several departments, we can immediately talk about widespread osteochondrosis of the spine.
Risk factors and causes of the disease
The spine has high strength and the development of the disease requires the action of several provoking factors at once. It is important to understand that most, if not all, of these factors can be influenced by the patient and thus reduce the likelihood of developing the disease.
- lack of movement - this worsens the blood supply, and hence the nutrition of all elements of the spine;
- excessive physical activity is also harmful and can damage the intervertebral discs;
- long stay in the wrong, not physiological position - the inappropriate height of the desktop or chair leads to the fact that a person is forced to constantly tilt his head, hunch over;
- stress - excessive tension in the muscles can lead to compression of the vessels that feed the spine;
- overweight;
- smoking impairs microcirculation in all tissues of the body;
- insufficient intake of water and protein also affects the condition of the intervertebral discs.
The immediate causes of osteochondrosis of the spine are not always obvious, but the following options can be distinguished:
- hereditary predisposition - genetically programmed features of cartilage and bone tissue, in which the wear process is faster;
- spinal injuries - a variety of complications can develop at the site of injury, including osteochondrosis;
- occupational hazards, such as vibration;
- exposure to infections or chemicals;
- natural aging of the body.
People of various professions are at risk for the development of osteochondrosis of the spine. These are builders and athletes, surgeons and office workers.
Stages of osteochondrosis and possible complications
The description of the four stages of osteochondrosis of the spine was proposed by Osna in 1971. They are not used to formulate a diagnosis, but allow you to understand how the disease proceeds.
- Intervertebral discs become less elastic. The disc may be slightly deformed, there is a shift of the internal pulpous nucleus within the disc. This stage either does not manifest itself in any way, or there are minor pains.
- At the second stage, cracks may appear in the disc, and the surrounding ligaments may weaken. The connection of the vertebrae becomes unstable. There are attacks of acute pain with disability.
- The third stage is characterized by complete damage to the intervertebral disc. When the nucleus pulposus leaves the disc, a herniated disc occurs. Spinal deformity or nerve root entrapment may occur.
- At the fourth stage, the surrounding tissues are affected - vertebrae, ligaments, spinal membranes. As a result, the vertebral segment can completely lose mobility.
As a result of spinal osteochondrosis, various complications occur in some cases. Problems with the intervertebral discs, hernia and protrusion can lead to narrowing of the spinal canal, compression of the spinal cord and disability.
Depending on the level of the lesion, various problems with the involvement of the nerve roots are possible. These are intercostal neuralgia, violations of sensitivity and motor function of the upper and lower extremities, disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. Inflammation of the sciatic nerve, or sciatica, not only causes severe pain, but can also lead to pelvic organ disease and infertility.
In addition to the nerve roots, osteochondrosis can compress the vertebral vessels. If blood flow is disturbed in the vertebral arteries that pass in the cervical region and feed the brain, brain disorders, problems with vision or hearing, breathing or cardiac activity may develop.
Approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of osteochondrosis: conventional and alternative methods
Within the framework of official medicine, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis includes an examination by a neurologist to determine the degree of damage to the nerve roots, checking reflexes and sensitivity.
Of the instrumental methods, the following can be used:
- Ultrasound of the vessels allows you to identify the degree of circulatory disorders, for example, in the vertebral arteries;
- X-ray of the spine;
- CT also uses radiological methods, but allows you to build a three-dimensional image of the area under study, to identify even small displacements of the vertebrae;
- MRI specializes in the study of soft tissues, allows you to assess the condition of the spinal cord, visualize the internal structure of the intervertebral disc.
For differential diagnosis, laboratory tests, a general blood and urine test, and indicators of calcium metabolism are used.
Therapy of osteochondrosis is complex.
- The first and very important tool in the treatment of osteochondrosis is lifestyle. Normalization of working conditions, moderate and regular exercise, as well as healthy sleep significantly improve the condition of patients.
- For drug treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine, a neurologist or general practitioner may prescribe medications. Most often, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - this is the standard treatment for spinal osteochondrosis. They reduce pain and reduce inflammation. Muscle relaxants help reduce muscle spasm. Vitamins and antioxidants are prescribed to protect nerve tissue from damage. However, any drugs have side effects, for example, NSAIDs can adversely affect the stomach.
- In addition to medicines, physiotherapy is used, for example, massage for osteochondrosis of the spine, as well as manual therapy. In severe complications of osteochondrosis, surgery may be required, but it is prescribed only if there is no effect from long-term conservative treatment.
Treatment of osteochondrosis in classical medicine in most cases is a lengthy process and can have negative effects on human health.
So, a number of drugs, in particular analgesics and muscle relaxants (especially with a sedative effect), can be addictive, and some drugs adversely affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Alternatively, you can consider methods that are used, for example, in traditional Chinese medicine.
Traditional Chinese medicine is very popular all over the world, in many countries there are special centers and training courses. Approaches and methods of therapy in the Celestial Empire differ from the usual, European view of the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
All diseases are considered as a violation of the balance and movement of Qi energy in the body, and therapeutic measures are aimed at restoring this balance. In China, various medicinal herbs, animal components, minerals, as well as various external influence methods such as acupuncture and acupressure are used.
These techniques have a wide range of indications and a minimum number of side effects.
Acupuncture
Synonymous names for this method are acupuncture, reflexology. The principle of treatment through acupuncture is to place needles on bioactive points. Each point is associated with the organ on which the impact is carried out.
Reflexology allows you to relieve tension and muscle spasms, has an anesthetic effect, helps to reduce pain. The method is safe, as most doctors use disposable sterile needles.
And in the case of using needles coated with gold or silver, they must be sterilized without fail. Feelings during the procedure depend on individual susceptibility, the patient may experience tingling or numbness.
It is important that the procedure is carried out by a highly qualified specialist with extensive experience. Improper needle placement will be useless or even harmful. In some cases, acupuncture is combined with exposure to weak doses of electric current.
Moxibustion
This is a specific way of influencing active points with the help of special wormwood cigars. The principle of action is similar to acupuncture and is often used in combination. A smoldering cigar is installed on the body in a special wooden house, while the active points are heated. Wormwood has a disinfecting, soothing and relaxing effect.
This method is safe because the glowing part of the cigar does not come into contact with the skin, although in some parts of China direct methods are used that act on the skin.
Massage
Massage therapy in China is practiced by several different schools. They use rotation techniques, pressing with one finger, manual therapy methods. Traditional massage techniques allow you to work out muscles and joints, as well as indirectly affect other organs and tissues, and help increase the body's defenses.
qigong
Traditional Chinese gymnastics, like massage, has several schools. Qigong movements, smooth, stretching and twisting, are great as exercises for the spine with osteochondrosis.
Qigong techniques do not require special equipment and can be performed at home.
However, before that, it is best to choose the right exercises with your doctor, as well as work out the correct execution technique under the guidance of a qualified specialist.
The level of science and medicine in China is very high, the combination of tradition and innovation gives amazing results. An example of the achievement of Chinese science is the methods of DNA therapy and DNA vaccines - these are the methods that are currently being used to develop cancer treatments and fight HIV.
Osteochondrosis of the spinal column in the elderly. Features of rehabilitation
People age differently: some retain a clear mind, are optimistic about life situations, and are cheerful. Others, having crossed the retirement age, lose interest in life.
- The rate of aging of the body depends on many factors, these are:
- 1) the genetic program for the development and decay of the organism;
- 2) the impact on a person of various, adverse life events.
- An adverse effect on a person is produced by poor housing conditions, harmful working conditions, living in an unfavorable climate, the inability to receive full-fledged medical and social assistance in time, an unhealthy lifestyle (malnutrition, bad habits, and prolonged emotional stress).
- When organizing treatment and rehabilitation measures for the elderly, it is necessary to take into account age-related and functional changes in this period of life.
- With aging, the volume of muscle mass decreases, the contractility of muscles weakens, changes occur in all parts of the spinal column.
Cervical osteochondrosis. The primary stage of the disease does not require special treatment. Standard preventive measures are able to cope with the pathology at this stage.
The greatest danger is the violation of the blood circulation of the brain, leading to a general disorder of functions and the formation of numerous foci of necrosis of brain tissues.
Prevention
Regardless of the chosen methods of treatment, the prevention of osteochondrosis plays an equally important role. What can be done for the health of the spine:
- drink enough water;
- control weight, do not overeat;
- choose the right shoes, if necessary - orthopedic insoles;
- choose a good mattress for sleeping, not very soft and giving sufficient support to the spine;
- eat foods rich in collagen (fish, turkey, aspic, various jellies);
- do regular exercise;
- adjust the height of the desktop and chair, taking into account growth.
As far as alternative methods of prevention are concerned, massage, qigong, and acupuncture have all worked well, for reasons that are quite understandable and described above.
It is important to remember that back pain can and should be dealt with. In order to change your lifestyle, it is not necessary to wait for the first signs of illness.
You can now get up from the computer, stretch your neck, include walks or massages in your to-do list.
And if osteochondrosis of the spine has become a problem that prevents you from living in peace, then the joint efforts of science and traditional medicine will help restore health and the joy of movement.